Intro
Choosing the wrong rubber material can lead to costly reorders, product failures, and strained supplier relationships. For procurement professionals, understanding the core differences between silicone and EPDM rubber is essential. This guide simplifies your decision with clear, side-by-side comparisons tailored for industrial use cases.
Silicone rubber performs best in high-temperature environments, withstanding -60°F to +390°F, while EPDM rubber handles -40°F to +250°F and excels in UV, ozone, and weather resistance. Silicone is ideal for cleanrooms, electronics, and medical use, whereas EPDM is more cost-effective and durable for outdoor and automotive sealing. Choosing between them depends on application-specific needs like temperature range, exposure, and required longevity.
Now that you know the basics, let’s break down the key differences between silicone and EPDM rubber in detail—so you can choose the right material with confidence and clarity.
1. What is the difference between EPDM and silicone rubber?
Silicone rubber and EPDM rubber are two of the most widely used elastomers in industrial manufacturing, but they serve very different functions based on their chemical composition and performance properties. Understanding these differences is critical for procurement professionals who need to balance performance, cost, and longevity in product design and supplier selection.
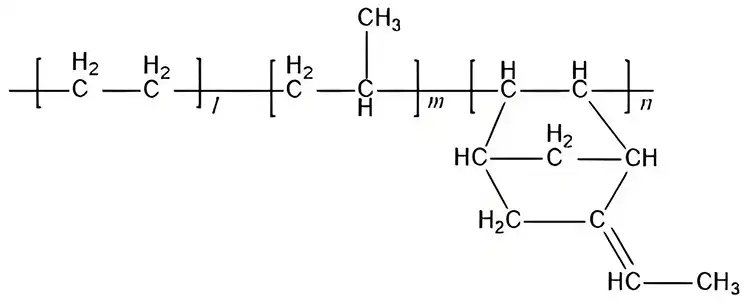
Representation of the chemical structure of EPDM.
Material Composition & Structure
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a synthetic rubber made from ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer. This structure gives it excellent resistance to outdoor elements such as UV rays, ozone, and moisture. It’s a non-polar elastomer, making it unsuitable for contact with oils, fuels, or many solvents.
- Silicone Rubber (Polysiloxane) is made from a backbone of silicon-oxygen chains, which gives it exceptional flexibility and stability across a wide temperature range. It is a semi-organic elastomer, and its inertness makes it highly suitable for medical, food-grade, and electronic applications.
Temperature Resistance
- Silicone operates in extreme environments, withstanding temperatures from -60°F to +390°F (and even higher in specialized grades). It remains flexible and stable in both cryogenic and high-heat conditions.
- EPDM has a more moderate range of -40°F to +250°F. While this is sufficient for most general industrial and outdoor applications, it cannot match silicone in high-heat resistance.
Environmental & Weathering Performance
- EPDM is highly resistant to UV radiation, ozone, and aging caused by weather exposure, making it ideal for roofing systems, automotive weather stripping, and outdoor gaskets.
- Silicone, although also resistant to environmental degradation, may not match EPDM’s outdoor durability in all applications, particularly those involving mechanical stress or abrasion.
Chemical Compatibility
- Silicone offers strong resistance to water, oxidation, and many chemicals, including some acids and bases, but it can swell or degrade in contact with fuels and oils.
- EPDM is excellent for steam, water, and many alcohols, but like silicone, it performs poorly in oil- or hydrocarbon-rich environments.
Summary for Buyers
- Choose EPDM for low-cost, high-durability applications in outdoor or automotive environments.
- Choose silicone when high heat resistance, inertness, or medical/electronic compliance is required.
![]()
2. Which is more durable, silicone or EPDM?
When it comes to durability, the better material depends heavily on the application environment. Procurement professionals should assess not only mechanical strength but also exposure conditions such as UV, temperature fluctuations, chemical contact, and mechanical stress.
Mechanical Strength
- EPDM rubber generally exhibits higher tensile strength and tear resistance than silicone. It also offers better abrasion resistance, which makes it suitable for high-wear environments like door seals, roofing systems, and outdoor gaskets that experience frequent friction or impact.
- Silicone, while flexible and stable under extreme temperatures, is inherently softer and more prone to tearing or mechanical damage. Its tensile strength ranges from 200 to 1,500 PSI (depending on grade), which is typically lower than that of EPDM.
Environmental Exposure
- EPDM is particularly durable in outdoor environments. Its resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and oxidation means it maintains integrity for years in sun-exposed or weather-intensive applications. For automotive weatherstripping or HVAC sealing, EPDM often outlasts alternatives.
- Silicone performs exceptionally well in thermal cycling, resisting both hardening and cracking in high-heat or freezing conditions. However, in abrasive or high-load environments, its lifespan can be shorter unless reinforced with fillers or coatings.
Lifespan in Use
- In mechanically demanding environments (e.g., dynamic seals, exterior exposure), EPDM often offers a longer service life.
- In high-temperature or sterile environments (e.g., ovens, cleanrooms, medical devices), silicone’s heat resilience ensures lasting performance with minimal degradation.
Choose EPDM for rugged, weather-exposed, or friction-heavy conditions. Opt for silicone where long-term thermal stability or cleanliness is critical, even if mechanical durability is secondary.
3. Is EPDM rubber better than silicone for sealing?
The effectiveness of a rubber seal depends on more than just fit — it must resist compression set, retain elasticity, and maintain sealing performance under variable conditions. Both EPDM and silicone are widely used in sealing, but their advantages depend on where and how they’re used.
Compression Set & Recovery
- Silicone rubber has excellent compression set resistance, especially in high-temperature environments. It maintains elasticity even after prolonged compression, which is critical in static sealing applications like oven gaskets, autoclaves, or cleanroom door seals.
- EPDM also offers good compression set performance but can degrade faster under sustained high temperatures. However, it retains shape well in moderate-temperature and moisture-rich environments, making it a popular choice in HVAC duct sealing or exterior trim.
Air, Water & Weather Sealing
- EPDM excels in weatherproofing and water sealing. Its molecular structure makes it highly resistant to moisture absorption, UV, and ozone — ideal for outdoor seals, door gaskets, and window trims. It’s also frequently used in water system applications due to its reliable sealing under fluctuating pressures.
- Silicone, being more chemically inert, is better for sterile sealing—in food, medical, and pharmaceutical settings where cleanliness and non-reactivity are critical. It’s also preferred for applications requiring resistance to extreme temperatures during operation or sterilization.
For weather and water sealing, EPDM is typically superior. For high-temperature or sterile environments, silicone seals deliver longer-lasting performance with minimal deformation.
4. What are the pros and cons of EPDM vs silicone?
When selecting a rubber material, it’s critical to balance technical properties, operating conditions, and overall cost-effectiveness. Both EPDM and silicone bring distinct advantages and limitations to the table. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown to help procurement teams make faster, better-informed decisions.
📊 Quick Comparison Table
| Property | EPDM Rubber | Silicone Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40°F to +250°F | -60°F to +390°F |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent (ideal for outdoor use) | Good, but less abrasion resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent for water, steam, alcohols | Excellent for oxygen, ozone, mild acids |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | Poor | Poor |
| Mechanical Strength | High (durable, abrasion-resistant) | Moderate (soft, flexible) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Sterility/Medical Use | Limited (requires special grades) | Excellent (naturally inert) |
| Compression Set Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | Roofing, automotive seals, HVAC gaskets | Medical devices, electronics, bakeware |
Key Takeaways
- EPDM is the smart choice for outdoor applications where cost control and weather resistance are priorities.
- Silicone is better suited for high-temperature, sterile, or flexible-sealing needs, despite its higher material cost.
- Neither material is ideal for oil- or hydrocarbon-rich environments; alternatives like NBR should be considered for such cases.
5. How does EPDM vs silicone cost compare?
Cost is a crucial factor in material selection, but it’s important to consider both initial cost and total cost of ownership over the product’s lifespan. While silicone and EPDM differ significantly in price, each material can prove cost-effective depending on the application.
Raw Material and Production Cost
- EPDM rubber is generally more economical, with lower raw material costs and easier processing for both molding and extrusion. It’s widely available and used in high-volume industries like automotive and construction, which helps drive down pricing.
- Silicone rubber is typically 2 to 5 times more expensive per pound than EPDM. Its higher cost comes from more complex manufacturing, longer cure times, and the premium nature of the polymer itself.
Tooling and Processing Costs
- Both materials can be processed via extrusion and molding, but silicone often requires higher-grade tooling and longer cure cycles, particularly in liquid silicone rubber (LSR) applications. This can increase setup and tooling costs, especially for short production runs.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- EPDM offers great value for outdoor and industrial use due to its long lifespan in UV- and weather-exposed applications, requiring fewer replacements.
- Silicone, though expensive upfront, can reduce long-term costs in medical, electronic, or high-temp applications where frequent failure or regulatory non-compliance would be more costly than the material itself.
When durability, certification, or extreme temperatures are essential, silicone may justify its price. For high-volume or outdoor applications, EPDM delivers reliability at a much lower cost.
6. Are EPDM and silicone compatible in multi-material systems?
In complex products, combining multiple rubber types seems like a cost-effective way to leverage the strengths of each material. However, EPDM and silicone are chemically and mechanically distinct, and their compatibility in multi-material systems requires careful engineering.
Chemical Compatibility
- EPDM is a non-polar rubber, while silicone is semi-organic and inert. This means they have low natural adhesion to each other.
- When bonded directly, they often exhibit weak interfacial strength, unless specialized adhesives or co-molding techniques are used.
Co-Molding & Adhesion
- Achieving a reliable bond between EPDM and silicone typically requires:
- Surface treatments (e.g., plasma or corona treatment)
- Primers or coupling agents
- Mechanical interlocks or overmolding designs
- Even with adhesives, differences in thermal expansion and flexibility can lead to long-term separation if the assembly undergoes stress or temperature cycles.
Performance Conflicts
- Silicone remains stable in extreme heat, while EPDM begins to degrade.
- EPDM resists UV and ozone better in some mechanical uses, but silicone performs better in sterile or chemical environments.
- Using both materials in one application may create a performance mismatch, resulting in premature failure unless engineered with precision.
If both materials must be used, work closely with a manufacturer experienced in hybrid rubber assemblies. Pre-testing, proper adhesive systems, and design accommodations are essential for durability.

rubber for gasket sealing
7. What’s the best rubber for gasket sealing – silicone or EPDM?
Gaskets play a critical role in preventing leaks, ensuring pressure stability, and maintaining system integrity. The decision between silicone and EPDM for gasket use depends heavily on the operating environment and performance demands.
Compression Set & Long-Term Elasticity
- Silicone rubber has outstanding compression set resistance, which means it retains its shape and sealing force even after long-term static compression. This makes it ideal for gaskets that must perform under consistent clamping pressure — such as in sterile environments, cleanrooms, and medical equipment.
- EPDM, while slightly less resilient over time under compression, still performs well in dynamic or low-heat sealing environments — especially outdoors or in HVAC systems.
Temperature & Chemical Tolerance
- Silicone gaskets excel in applications with high temperature fluctuations or where materials must endure sterilization cycles (e.g., autoclaves, baking ovens, or pharmaceutical processing).
- EPDM gaskets offer strong resistance to steam, water, and glycol-based fluids, which is why they are frequently used in cooling systems, building facades, and irrigation components.
Regulatory & Safety Standards
- Silicone is preferred for FDA-, ROHS-, and USP Class VI-compliant gaskets in food or medical applications.
- EPDM is more commonly used in construction, automotive, and industrial equipment, where such compliance is not mandatory.
Use silicone for high-purity or high-temperature sealing, and choose EPDM for cost-effective, weather-resistant, and water-handling gaskets.
8. How do EPDM and silicone perform on rooftops or exterior use?
For rooftop systems, window seals, HVAC enclosures, and other exterior applications, rubber components must endure years of sunlight, moisture, ozone, and temperature swings without cracking, shrinking, or losing elasticity. Both EPDM and silicone can be used outdoors—but one is far more dominant in these environments.
UV and Ozone Resistance
- EPDM is one of the most UV-resistant synthetic rubbers available. It has a saturated polymer backbone that resists cracking and hardening under prolonged UV and ozone exposure. This makes it a top choice for roofing membranes, window gaskets, solar panel mounts, and weatherproof seals.
- Silicone also resists UV and ozone well, but is softer and more susceptible to abrasion and mechanical damage, especially in harsh outdoor environments. It may degrade faster if exposed to blowing debris, sand, or mechanical stress.
Weatherproofing and Temperature Extremes
- EPDM maintains performance across fluctuating temperatures and repeated wet-dry cycles. It resists water absorption and doesn’t become brittle in freezing conditions, making it reliable for roof flashing, RV and marine seals, and outdoor HVAC systems.
- Silicone can tolerate more extreme temperature ranges (-60°F to +390°F), but its flexibility offers diminishing returns outdoors unless the application involves little physical contact or wear.
Choose EPDM for rooftops, window trims, and any application exposed to sunlight, ozone, and moisture. Use silicone only if high heat or chemical resistance is also a requirement, and physical wear is minimal.

Car door sealing parts
9. EPDM vs silicone in automotive parts – which wins?
Automotive environments present some of the harshest operating conditions for rubber components: wide temperature fluctuations, exposure to oils and coolants, mechanical vibration, and outdoor elements. Selecting the correct material—EPDM or silicone—can have a direct impact on vehicle reliability, warranty claims, and total lifecycle cost.
Thermal Performance
- Silicone rubber maintains flexibility and sealing performance from -60°F to +390°F, making it ideal for high-temperature engine bay applications. It resists hardening, cracking, or melting when used near heat sources such as turbochargers, exhaust systems, or high-output lighting.
- EPDM performs well up to 250°F and is commonly used for cooling system hoses, windshield wiper seals, door and window weatherstripping, and under-hood electrical grommets where extreme heat is not sustained.
Chemical and Fluid Resistance
- EPDM offers excellent resistance to coolants, water, and steam, but it is not compatible with oils, fuels, or most hydrocarbons, which limits its use around engines or transmissions.
- Silicone also lacks resistance to oils and fuels unless specially compounded. In such cases, fluorosilicone may be used as a more suitable (but costly) alternative.
Mechanical Stress and Longevity
- EPDM has superior resistance to abrasion, tearing, and mechanical stress, making it ideal for dynamic seals, weatherstrips, and suspension boots that undergo frequent movement or impact.
- Silicone, while flexible, can be prone to tearing if not reinforced or properly supported—best suited for static sealing or controlled environments.
Use Case Guidance
- Choose EPDM for weather-exposed parts, window seals, and coolant systems.
- Choose silicone for high-temperature static seals or under-hood insulation, but avoid areas with oil exposure unless using specialty grades.
10. Should I choose EPDM, silicone, or neoprene rubber?
After understanding the core differences between EPDM and silicone, you might be wondering: where does neoprene fit into the equation? This section offers a simple, comparative decision guide to help you confidently select the right rubber material based on application-specific demands.
Material at a Glance
| Property | EPDM | Silicone | Neoprene |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40°F to +250°F | -60°F to +390°F | -20°F to +200°F |
| UV/Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | Poor | Poor (unless fluorosilicone) | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Low | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
| Common Uses | Auto seals, roofing, HVAC | Medical, electronics, baking | Industrial gaskets, wetsuits |
Decision Framework
- Choose EPDM if your application is outdoor, exposed to weather, or needs high durability at a low cost — think HVAC, automotive weather seals, irrigation systems.
- Choose Silicone if your product faces extreme temperatures or needs regulatory compliance for medical, food-grade, or cleanroom environments.
- Choose Neoprene if you need a middle ground: good general-purpose properties with better oil resistance than EPDM, at a cost lower than silicone. It’s often used in industrial gaskets, marine environments, and protective gear.
If you have questions, please contact us to understand your operating environment, required service life and compliance requirements. Each material performs well in different conditions, and the right combination can reduce failures and save costs in the long run.
Conclusion
Choosing the right rubber material is all about matching performance to purpose. EPDM, silicone, and neoprene each have their strengths—what matters is aligning them with your environment and performance goals. For expert advice, certification or custom samples, contact us to get the most suitable solution faster.
References:
- A Review of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Rubber: Properties, Applications, and Modifications
- Silicone Rubber – Wikipedia
- Study on mechanical properties of silicone rubber materials used as gaskets in PEM fuel cell environment
- Cleaning of aged EPDM rubber roofing membrane material for successful patch bonding
- Silicon Hybrid EPDM Composite with High Thermal Insulation and Mechanical Properties
