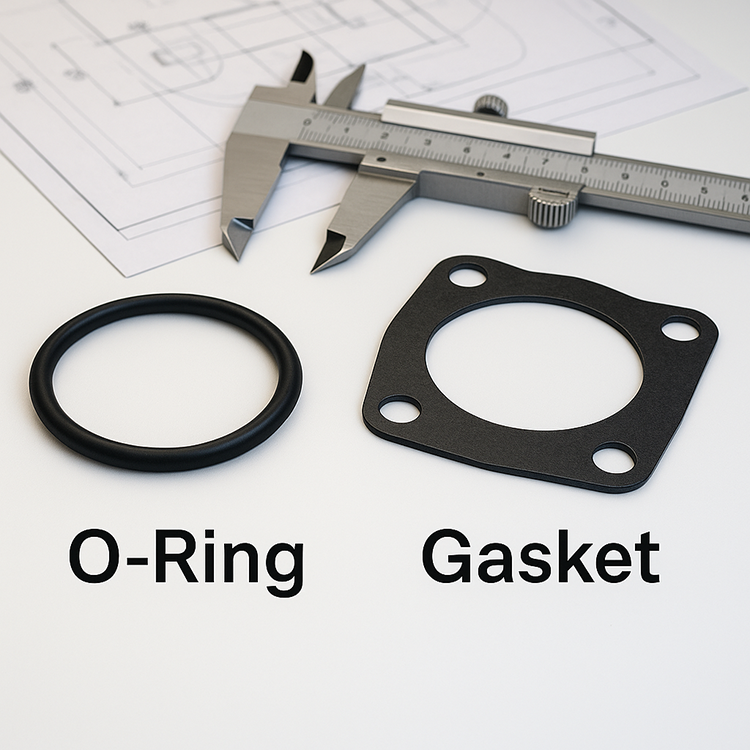
1. Definition and Shape
In my work with industrial buyers and engineers, I’ve noticed a common confusion: people often lump O-rings and gaskets into the same category. While they both serve the essential function of sealing joints to prevent leakage, they are fundamentally different in form and use.
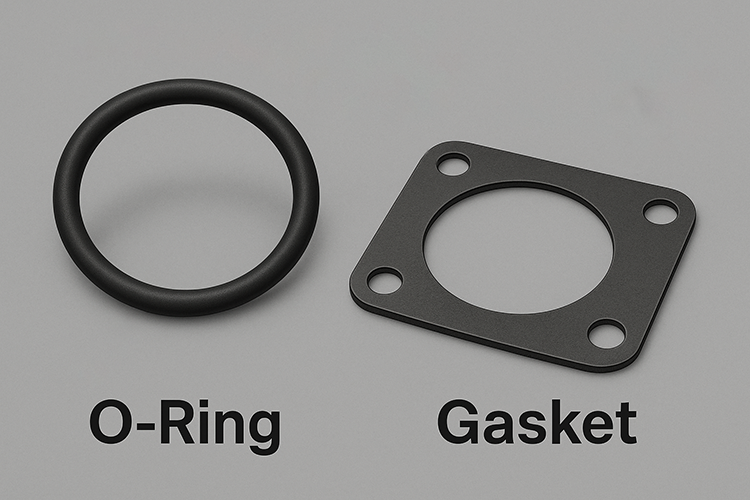
O-rings are circular sealing rings made from flexible elastomers. What makes them unique is their round cross-section and symmetrical shape, which allows them to create a tight seal when compressed inside a machined groove. They’re especially effective in dynamic environments—like moving pistons or rotating shafts—where maintaining pressure is critical.
Gaskets, on the other hand, are flat components that come in a wide variety of shapes—round, square, oval, or custom-cut. Their main job is to seal the space between two flat or uneven surfaces, such as flanges or engine blocks. Because they don’t rely on a groove to function, gaskets offer more design flexibility and are often cut to fit complex assemblies.
The key distinction lies in their geometry: O-rings seal by radial or axial compression in a groove, whereas gaskets fill the surface gap between two stationary parts.

2. Material Types
When selecting the right seal, material matters just as much as shape. I’ve seen many projects run into issues simply because the wrong material was chosen for the environment. O-rings and gaskets are made from different classes of materials, each suited for specific conditions.
O-rings are typically made from elastomers—rubber-like materials that can compress and rebound. Common options include:
- Nitrile (NBR): Affordable and oil-resistant, ideal for automotive or hydraulic applications.
- Silicone: Great for extreme temperature swings, often used in food-grade or medical settings.
- EPDM: Excellent for weather, ozone, and steam resistance.
- Fluorocarbon (Viton®): Chemically resistant and durable in harsh environments.
- PTFE (Teflon®) and thermoplastics: Used in chemically aggressive or high-friction applications where traditional rubber won’t last.
Gaskets, however, come in a much wider range of materials, because they are used in more diverse shapes and surface conditions. Depending on the need, they can be made from:
- Rubber: Such as silicone, EPDM, neoprene, or nitrile—good for flexibility and sealing.
- Metal: Stainless steel, copper, or aluminum—preferred for high-pressure or heat-intensive applications.
- Compressed fiber: Used in steam, gas, or water sealing.
- Cork or paper: Ideal for low-pressure, low-temperature assemblies like electronics.
- Graphite and multi-layer composites: Used in ultra-high-temperature or corrosive environments like chemical plants.
O-rings favor flexibility and dynamic sealing, while gaskets offer adaptability for broader, more complex surfaces and demanding conditions.
3. Sealing Method and Applications
Understanding how each component seals is critical for selecting the right one. I’ve worked with clients in both dynamic machinery and static piping systems, and trust me—misapplying these seals can lead to costly downtime or dangerous leaks.
Let’s break it down in a comparison:
| Feature | O-Ring | Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Compressed in a groove between round parts | Fills space between two flat/mating surfaces |
| Best Suited For | Round, pressurized joints | Flat or irregular stationary joints |
| Application Type | Static & dynamic (rotary or reciprocating motion) | Static (no movement between surfaces) |
| Common Uses | Hydraulic cylinders, pumps, fuel lines, valves | Flanges, engine manifolds, HVAC ducts, pipe joints |
O-rings perform exceptionally well in high-pressure systems and can even maintain a seal under motion—making them a top choice for hydraulic pistons, rotating shafts, and valve stems. Their strength lies in their simplicity and ability to deliver a uniform seal across symmetrical geometries.
Gaskets, on the other hand, excel in static sealing applications. Because they can be cut to any shape and thickness, they’re ideal for covering wide surface areas—like between engine covers, piping flanges, or access panels. Their flexibility makes them perfect for sealing uneven or imperfect surfaces.
If your joint involves movement, pressure, and a groove—go for an O-ring. For flat, static surfaces or irregular outlines—gaskets win every time.
4. Performance Characteristics
When performance is on the line—whether in an engine compartment, chemical processing plant, or food-grade assembly line—the choice between O-rings and gaskets isn’t just about fit. It’s about how each performs under pressure, temperature, and movement.
O-Rings
- Outstanding for high-pressure systems: Their circular shape allows uniform compression, creating a tight seal that withstands hundreds—even thousands—of PSI.
- Reliable under dynamic motion: They flex with rotary or reciprocating shafts, which makes them ideal for hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.
- Requires precision: O-rings must be installed in carefully machined grooves to avoid issues like twisting, pinching, or extrusion under load. Even a slight misfit can compromise the entire seal.
Gaskets
- Engineered for chemical and thermal extremes: Depending on the material—like graphite or metal gaskets—they can handle temperatures above 500°C and aggressive chemicals.
- Excellent for large, flat, or irregular surfaces: They conform to surface imperfections and maintain their seal over broader areas.
- Less pressure resistant than O-rings: Gaskets aren’t built for deep compression; they seal through surface contact rather than internal stress.
O-rings thrive in pressure and motion, while gaskets dominate in heat, chemical resistance, and surface adaptability.

5. Installation and Maintenance
When it comes to installation and long-term care, I always advise clients to weigh not just the sealing performance, but also the practicality of upkeep—especially in systems that require frequent maintenance or part replacements.
| Feature | O-Ring | Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Simple; fits into a machined groove | May require careful alignment and correct bolt torque |
| Replacement | Quick and easy in most cases | Can be time-consuming, especially in large assemblies |
| Maintenance Tip | Use compatible lubricants to prevent tearing or pinching | Always check for surface flatness and clean mating areas |
O-rings are generally easier to install. Once the groove is clean and the O-ring is lubricated with a suitable compound (such as silicone grease), it simply drops into place. However, even a minor twist or over-stretch during installation can lead to seal failure—so proper technique is essential.
Gaskets require a bit more finesse. Since they lack the structural containment of a groove, their sealing success depends on how precisely they align with the surfaces and how evenly the bolts are torqued. Overtightening can crush the gasket, while undertightening may cause leaks.
In service-heavy environments, O-rings offer speed and simplicity, but for complex interfaces, gaskets provide more sealing options—at the cost of longer setup and inspection times.
6. Summary Table
Here’s a quick-reference comparison I often share with clients when they’re deciding between O-rings and gaskets. It condenses everything we’ve covered so far into a clear, actionable guide:
| Feature | O-Ring | Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Round cross-section ring | Flat, can be any custom shape |
| Material Range | Mostly elastomers, some PTFE/plastics | Rubber, metal, fiber, cork, graphite, etc. |
| Sealing Style | Radial or axial compression in a groove | Surface compression between flat faces |
| Best For | Pressurized, dynamic or round joints | High-temp, static, or irregular surface joints |
| Installation | Needs a precision groove | Needs surface prep and accurate torqueing |
This table helps clarify one key takeaway: O-rings specialize in mechanical sealing with minimal surface area, while gaskets offer flexibility and coverage for large or oddly-shaped interfaces.
7. Conclusion
After two decades in the rubber sealing industry, I’ve come to see O-rings and gaskets not as rivals—but as complementary tools. Each has its strengths, and each excels under different operating conditions.
O-rings are engineered for precision: they’re the go-to choice for high-pressure, round interfaces, especially when motion or vibration is involved. Their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for compact, dynamic systems like hydraulic pistons or valve assemblies.
Gaskets, on the other hand, are unmatched in versatility and surface adaptability. Whether sealing an engine manifold, a pipe flange, or an HVAC duct, gaskets offer the design flexibility and material options needed for static, high-temperature, or chemically aggressive environments.
If the application involves movement, pressure, and a groove—go with an O-ring.
If it’s flat, irregular, and static—trust a well-cut gasket.
Choosing the right seal isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a performance safeguard. Understand your geometry, media, pressure, and temperature, and the right choice will protect your system for years to come.
Need Help Choosing the Right Seal?
At Kinsoe, I specialize in custom rubber sealing solutions—from precision-molded O-rings to high-performance gaskets for industrial applications. If you’re unsure which type is best for your project, I can help evaluate your requirements and recommend the most effective and economical option.
Contact me today for expert support, free consultation, or a fast quote tailored to your design specs.
References: